Computer Networks
Computer networks means, an interconnected set of
autonomous computers. The term autonomous means that the computers can function
independent of each other’s. However, the computers can exchange information
with each other through the communication network system.
Computer networks are emerged as a result of
convergence of two technologies computer
and communication.
History
One of the most significant developments was the ARPANET (Advanced Research Project
Agency Network).The ARPANET was start with only four nodes as an experimental
network in 1969. The University of California
at Los Angeles, the Stanford Research Institute, University of California
at Santa Barbara, and
the University of Utah were connected as the beginning of the ARPANET network using 50 kbit/s circuits. It has
subsequently grown into a network of several computers spanning across the
world. Some of the present day concept like packet switching evolved from the ARPANET project. One of the
problems with early computer
networks was the bandwidth. In the
later years, use of satellite communication and use of fiber optics allowed
high-speed data communication over large distance. Today, computer networks are
the core of modern communication.
Some Properties of computer Networks
·
Permit sharing of files, data, and other
types of information
·
Facilitate communications
·
Share network and computing resources
Network Technologies
There is no generally accepted taxonomy into which all computer networks fit, even though there exist two general classification that are transmission technology and scale.Network Transmission Technology
Classification of networks based on transmission technology
Based on the transmission technology
computer networks are classified into two.
1. Broadcast Networks
2. Point-to-Point networks
Broadcast Networks
Broadcast network have a communication channel that is
share by all the nodes in the network. BUS network is an example of broadcast
network.
 |
| BUS network |
All
the nodes on the network receive the messages sent by any machine in broadcast
network. An address field of the message determines the intended recipient.
Upon receiving a message, the node checks the address field of the message. If
the message is intend to itself then process the packet otherwise it simply
ignore the packet.
Broadcasting refers to a method of
transferring a message to all recipients simultaneously. Some broadcast system
also support multicasting. Multicasting
means send data to a subset of nodes in the network.
 |
| Broadcasting |
 |
| Multicasting |
Point-to-point Networks
In the
case of point-to-point network, there exist many connections between individual
pairs of nodes. A transmitted packet may visit some intermediate node before
they actually reach its destination. There may multiple routes between two
nodes so routing algorithms play an important rule in point to point networks.
The
connection between two nodes either one of the following
1.
Dedicated
2.
Shared
In the
case of dedicated connection, there exist a dedicated connection between sender
and receiver. Three types of dedicated connections are there
a.
simplex
b.
half duplex
c.
duplex
Simplex connections only allow
the transmission of data in one direction. Radio and TV are examples. In contrast, links that can be used
in either direction, but only one way at a time, like a single-track railroad
line are called half-duplex links. CBZ radio is a half-duplex device.
Links that can be use in both directions at the same time, like a two-lane
road, are call full-duplex links. Point-to-point transmission with one sender and one receiver
is sometimes call unicasting.
Network Technologies Based on Scale
Based on scale networks
are classified into
1.
Local area network(LAN)
2.
Metropolitan area network(MAN)
3.
Wide area network(WAN)
Local Area Network (LAN)
A local area network (LAN) is a computer network that interconnects computers in a limited area such as a
home, school, or office building using network media. LAN is normally private
owned. These are use to exchange information and to share resources (both
hardware and software). The defining characteristics of LANs, in contrast to other networks, include their size,
transmission technology and topology.
The most common LAN topology is bus, ring and
star.
Metropolitan Area Network
A metropolitan area network (MAN) is a computer network that usually spans a city or a large campus. It may be a
single network or it may be means of connecting a number of LANs into larger
network so that resources may be share. Cable TV network is an example of MAN.
There
exist a standard for MAN, that is DQDB
(Distributed Queue Dual Bus) or IEEE
802.6
Wide Area Network (WAN)
A Wide Area Network is a
network that covers a large geographical area may comprise a country, continent
or even the whole world. WAN allows transmission of data and information across
a large geographical area.
The Internet
The
Internet collection of networks or network of networks that consists of millions of private,
public networks, of local to global scope, that are linked by a broad array of
electronic, wireless and optical networking technologies. The networks
are connecting through suitable hardware and software in seamless manner.
The basic
difference between WAN and Internet is that WAN is owned by single organization
while Internet is not so.
Network Topology Bus, ring and star
Network Topology
The term topology
refers to the way a network is laid out, either physically or logically. Physical topology refers to the
placement of the network's various components, including device location and
cable installation, while logical topology shows how data flows within a network, regardless of its
physical design. We will briefly discuss various topologies of LAN.
Bus Topology
Bus
topology is an implementation of broadcast networks. In bus topology, a single
long cable acts as a backbone to link all devices in the network.
Advantages
·
Ease of installation
·
Cheap and simple
·
Uses less cables
Disadvantages
·
Difficulty in fault tolerance and reconfiguration.
·
A break in the cable stops all transmissions.
Ring Topology
In ring topology, each node has a dedicated
point-to-point connection only with the two nodes in either side of it. A
message or signal is passed along the ring in one direction, from device to
device, until it reaches its destination.
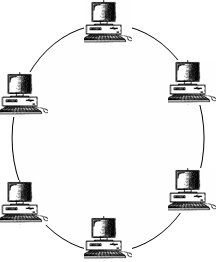 |
| Ring Topology |
Advantages
·
Easy to install and reconfigure
·
Fault isolation is simplified
·
Perform better than bus topology under heavy load
Disadvantages
·
Unidirectional traffic
·
A break in the ring can disable the entire network
Star Topology
Star networks are the most common LAN
topology. In a star topology, each device has a dedicated link inly to a
central controller, usually the hub. All data exchange between devices take
place through hub.
 |
| Star topology |
Advantages
·
Better performance
·
Isolation of devices
·
Benefits from centralization
Disadvantage
of the star topology is that if the
central controller fails, the entire network goes down with it.
Network Topology Tree and Mesh
Tree topology
In tree
topology a central 'root' node (the top
level of the hierarchy) is connected to one or more other nodes that are one
level lower in the hierarchy (i.e., the second level) with a point-to-point
link between each of the second level nodes and the top level central 'root'
node. Means nodes in a tree are link to central hub that controls the traffic
to the network but not every device plugs directly to the central controller.
Most of the devices are connect to some secondary hub, which in turn connected
to central hub.
 |
| Tree topology |
A very good example
of tree topology is the cable TV network.
Advantages
·
Scalable
·
More manageable (because, of different levels of network).
Disadvantages
·
Maintenance may b an issue
Mesh Topology
In mesh network
topology every nodes has a dedicated connection to every other nodes. The
dedicated connections in the mesh topology only caries the traffic between two
devices it connects. A fully connected mesh topology has n(n-1)/2 physical channels to link n devices. To manage this much
links very device on the network must need (n-1) input output ports.
 |
| Mesh topology |
Advantages
·
Secure
·
Robust
·
Eliminate traffic problems
Disadvantages
·
Many ports are needed in each device
·
Installation and reconfiguration are difficult
·
Expensive due to huge cabling
No comments:
Post a Comment